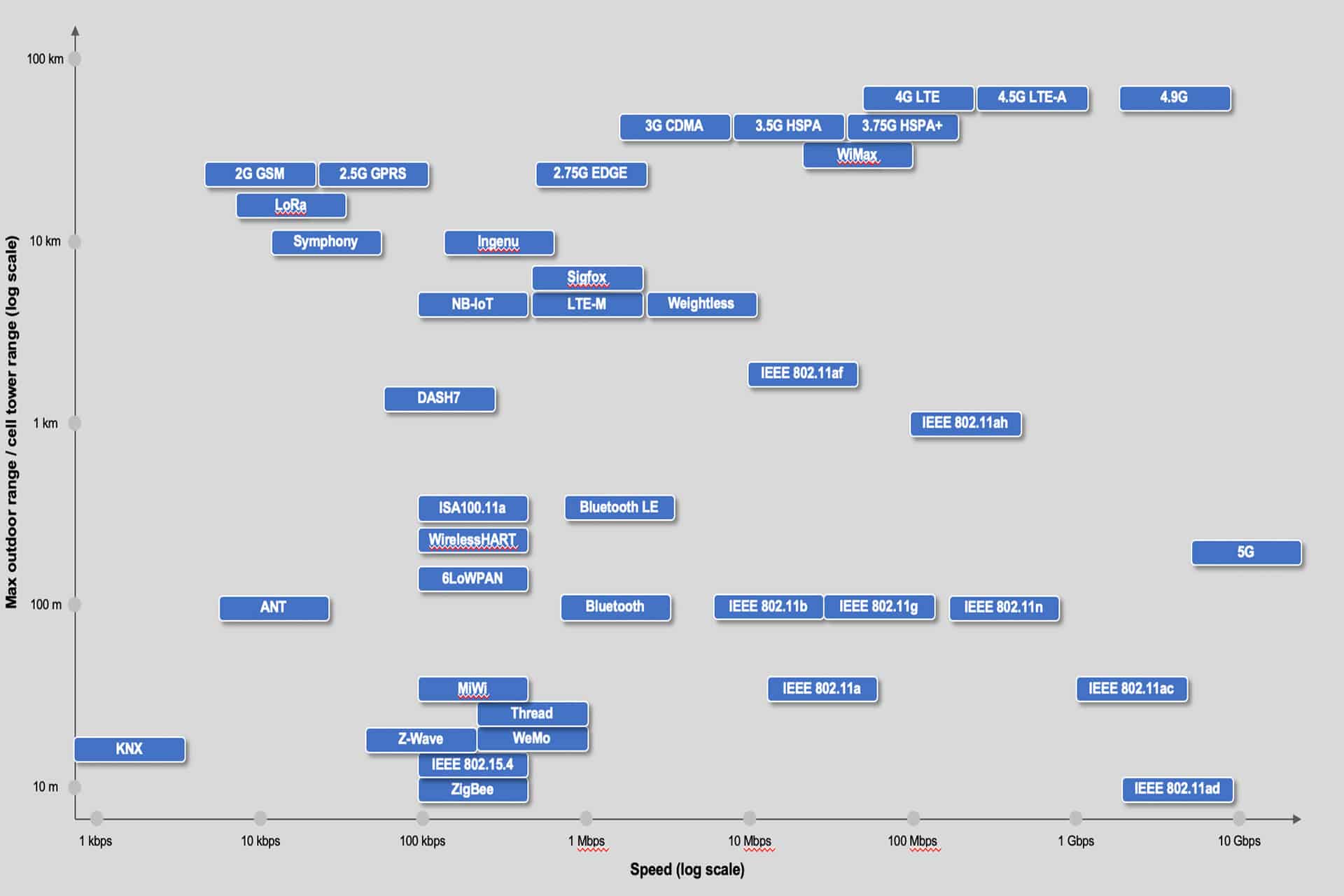
IoT Wireless Protocols - Speed & Range
| wdt_ID | Wireless technology / standard | Data Rate | Approximate Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5G | Low-band 5G (600 - 700 MHz) giving download speeds a little higher than 4G at the moment: 30-250 Mbps. Mid-band 5G (2.5-3.7 GHz) currently allowing speeds of 100-900 Mbps. High-band 5G (25 - 39 GHz and higher frequencies up to 80GHz) achieves, at the mom | Range is correlated with frequency bands - low band 5G has similar range to 4G (tens of kilometers), Mid-band 5G has several km range. High-band 5G has hundreds of meters up to 1.5 km range. |
| 2 | ANT+ Alliance | 12.8 Kbit/s - 60kbit/s | ≈ 30m |
| 3 | Bluetooth | ≈ 2Mbps | ≈ 50m |
| 4 | BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) or Bluetooth Smart (Bluetooth 5, 4.2) | <1Mbps ≈ (n x 100kbps) | ≈ 100m |
| 5 | GSM/GPRS/EDGE (2G), UMTS/HSPA (3G), LTE (4G) | Typical download: 35-170kps (GPRS), 120-384kbps (EDGE), 384Kbps-2Mbps (UMTS), 600kbps-10Mbps (HSPA), 3-10Mbps (LTE) | ≈ 35km max for GSM and ≈ 200km max for HSPA |
| 6 | IEEE 802.15.4 | ≈ 20 kbps and 40 kbps (BPSK ), ≈ 250 kbps (O-QPSK with DSSS) | ≈ 100m |
| 7 | ISA100.11a | ≈ 250 kbps | ≈ 100m |
| 8 | 6LoWPAN | ≈ 250 kbps | ≈ 100m |
| 9 | LoRaWAN | ≈ 0.3-50 kbps | ≈ 15km |
| 10 | EC-GSM-IoT | 70 kbps (GSMK), 240 kbps (8PSK) | ≈ 15km |
| 11 | LTE-MTC Cat 0 | ≈ 1 Mbps | Range is variable and depends on frequency bands, propagation conditions etc. typically it is ≈ 10km |
| 12 | LTE-M (Cat M1, Cat M2 ) - eMTC | LTE-M Cat M1 ≈ 1 Mbps LTE-M Cat M2 ≈ 4 Mbps DL / ≈ 7 Mbps UL | Range is variable and depends on frequency bands, propagation conditions etc. typically it is ≈ 10km |
| 13 | NB-IoT - Narrowband-IoT (LTE Cat NB1 and LTE Cat NB2) | LTE Cat NB1 ≈ 66 kbps (multi-tone) and ≈ 16.9 Kbit/s (single-tone) LTE Cat NB2 ≈ 159kbps | Range is variable and depends on frequency bands, propagation conditions etc. typically it is better than LTE-M coverage. |
| 14 | Neul | up to 100kbps | ≈ 10km |
| 15 | NFC | 106kbps, 212kbps, 424kbps | ≈ 10cm |
| 16 | RPMA (Random Phase Multiple Access) | 100kb | ≈ 70km |
| 17 | IEEE 802.11a/b/g/n/ac | Different data rates are enabled in IEEE 802.11 family of standards and their theoretical throughput is 11 Mbps ( IEEE 802.11b), 54 Mbps (IEEE 802.11a and IEEE 802.11g), 100 Mbps (IEEE 802.11n) or 300 Mbps (IEEE 802.11ac). | ≈ 50m |
| 18 | IEEE 802.11ah (Wi-Fi HaLow ) | 347Mbps | ≈ 900m |
| 19 | IEEE 802.16 (WiMax) | 40Mbit/s - mobile, 1 Gbit/s - fixed | ≈ 50km |
| 20 | HART | 250 kbps | ≈ 200m |
| 21 | Z-Wave | 40kbps (915MHz) and 20kbps (868MHz) | 30-100m |
| 22 | ZigBee | 250 kbps (2.4GHz) 40kbps (915MHz) 20kbps (868MHz) | 30-100m |
| 23 | Thread | 250kbps | ≈ 30m |
| 24 | DigiMesh | 250 kbps (2.4) 40kbps (915) 20kbps (868) | ≈ 100m |
| 25 | MiWi | 20kbps | ≈ 300m |
| 26 | EnOcean | 125kbps | ≈ 30m (outdoor 300m) |
| 27 | Weightless (W, N, P) | ≈ 600bps-100kbps | ≈ 2km (P), 5km (W, N) |
| 28 | mcThings | 50kbps | ≈ 200m |
| 29 | LoRa | 50kbps | ≈ 30km |
| 30 | SIGFOX | 600bps | ≈ 40km |
| 31 | DECT ULE | 1Mbps | ≈ 300m |
| 32 | Insteon | 38400bps - via RF 13165bps - via powerlines | ≈ 50m |
| 33 | RFID | 4kbps - 640kbps (depending on the active or passive type of device and frequency range). | 0.01m-10m (depending on the frequency range) |
| 34 | WAVIoT (NB-Fi - Narrowband Fidelity) | 10-100bps | ≈ 50km |
| 35 | DASH7 Alliance Protocol (D7A or D7AP) | 167kbps | ≈ 2km |
| 36 | Wi-SUN | 300kbps | ≈ 1000m |
| 37 | Wavenis | 9.6kbps (433 & 868MHz) / 19.2kbps (915MHz) | ≈ 1000m |
| 38 | MiOTY | 407 bps | ≈ 20km |
| Wireless technology / standard | Data Rate | Approximate Range |
For over 30 years, Marin Ivezic has been protecting people, critical infrastructure, enterprises, and the environment against cyber-caused physical damage. He brings together cybersecurity, cyber-physical systems security, operational resilience, and safety approaches to comprehensively address such cyber-kinetic risk.
Marin leads Industrial and IoT Security and 5G Security at PwC. Previously he held multiple interim CISO and technology leadership roles in Global 2000 companies. He advised over a dozen countries on national-level cybersecurity strategies.